- Stars are so far away that we have no hope of ever reaching them.
So how can we learn about the temperature of stars?- by comparing the brightness of very many of them
- by returning a sample of star material to the earth
- by plotting an distance-brighntess nomogram
- by studying the color of the star
- Compare the temperature of the red star Antares with the temperature of our yellow star, the Sun.
- Antares is cooler than the Sun.
- The Sun is cooler than Antares.
- Temperature cannot be determined with the information given.
- With a spectroscope you can see an emission spectrum when you look at a tube of hot glowing gas.
What does an emission spectrum look like?- continuous colors of the rainbow
- dark lines in a background of continuous colors
- certain bright colored lines
- a single bright sphere of color
- With a spectroscope you can see an absorption spectrum when you look at a cool gas with a light source behind it.
What does an absorption spectrum look like?- continuous colors of the rainbow
- dark lines in a background of continuous colors
- certain bright colored lines
- a single bright sphere of color
- With a spectroscope you can see an continuous spectrum when you look at a hot, solid, glowing object.
What does an continuous spectrum look like?- continuous colors of the rainbow
- dark lines in a background of continuous colors
- certain bright colored lines
- a single bright sphere of color
- You are using a spectroscope to look at a hot, glowing, solid object.
Between you and the hot object is a tube with some cool gas in it.
What type of spectrum will you see?- a continuous spectrum
- a flash spectrum
- an absorption spectrum
- an emission spectrum
- You are using a spectroscope to look at a hot, glowing, solid object.
What type of spectrum will you see?- a continuous spectrum
- a flash spectrum
- an absorption spectrum
- an emission spectrum
- You are using a spectroscope to look at a hot, glowing gas.
What type of spectrum will you see?- a continuous spectrum
- a flash spectrum
- an absorption spectrum
- an emission spectrum
- A bushed-looking astronomy student walks into class mumbling, "Oh Be A Fine Guy, Kiss Me".
What is she trying to remember?- the spectral classes of stars from hottest to coolest
- the spectral classes of stars from coolest to hottest
- the temperatures of the nearest stars
- the seven brightest stars in our night sky
- Which is hotter, a K3 star or a F5 star?
- K3
- F5
- Which sequence of spectral types (from hottest to coolest) is incorrect?
- O, B, F, M
- A, F, G, K
- B, A, K, M
- B, F, O, G
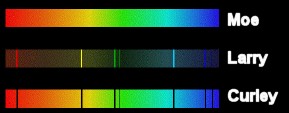
Which of these is an emission spectrum?- Moe
- Larry
- Curley

Which of these is an absorption spectrum?- Moe
- Larry
- Curley

Which of these is an continuous spectrum?- Moe
- Larry
- Curley
- A bushed-looking astronomy student walks into class mumbling, "Roy G Biv".
What is she trying to remember?- the colors of the visible spectrum from longest wavelangth to shortest wavelength
- the colors of the visible spectrum from shortest wavelangth to longest wavelength
- the temperatures of the nearest stars
- the seven brightest stars in our night sky
- A bushed-looking astronomy student walks into class mumbling, "Roy G Biv".
What is he trying to remember?- the colors of the visible spectrum from highest energy to lowest energy
- the colors of the visible spectrum from lowest energy to highest energy
- the temperatures of the nearest stars
- the seven brightest stars in our night sky
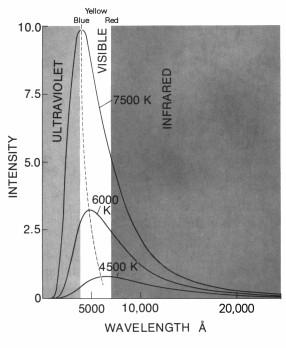 Wien's displacement law says that as a material gets hotter, the peak intensity of radiation given off by the object shifts toward shorter and shorter wavelengths of light.
Wien's displacement law says that as a material gets hotter, the peak intensity of radiation given off by the object shifts toward shorter and shorter wavelengths of light.
This means- a hot star will be "bluer" than a cooler star.
- a hot star will be "redder" than a cooler star.
- that all stars are white hot.

What is the color of a 7500 K object?- Blue
- Yellow-White
- Orange
- Red

What is the color of a 6000 K object?- Blue
- Yellow-White
- Orange
- Red

What is the color of a 4500 K object?- Blue
- Yellow-White
- Orange
- Red

What is the color of an object that emits at a peak of 5000 angstroms?- Blue
- Yellow-White
- Orange
- Red

What is the color of an object that emits at a peak of 7000 angstroms?- Blue
- Yellow-White
- Orange
- Red

What is the color of an object that emits at a peak of 4000 angstroms?- Blue
- Yellow-White
- Orange
- Red
- How would a yellow star appear different if it were to become hotter.
- It might become orange or red.
- It would become white or blue.
- It would become dimmer.
- It would not change in color or brightness.
- How would a yellow star appear different if it were to become cooler.
- It might become orange or red.
- It would become white or blue.
- It would become brighter.
- It would not change in color or brightness.

Other than color, how would an object at 4500 K appear different from an object at 7500 K?- The 4500 K object would be brighter than the 7500 K object.
- The 7500 K object would be brighter than the 4500 K object.
- The only difference would be color.
- They appear identical in every way.

Other than color, how would an object emitting at a peak of 4000 angstroms appear different from an object emitting at a peak of 7000 angstroms?- The object emitting at a peak of 4000 angstroms would be brighter than the object emitting at a peak of 7000 angstroms.
- The object emitting at a peak of 7000 angstroms would be brighter than the object emitting at a peak of 4000 angstroms.
- The only difference would be color.
- They appear identical in every way.
- Almost all stars are made of the same material (mostly hydrogen and some helium with traces of other elements or compounds.)
So why do stars have such a wide variety of different looking spectra?- The stars are of different temperature.
- The stars are of different brightness.
- The stars are made of different substances.
- All stars have very similar looking spectra.
- Why is it that only the coolest stars show molecular spectral lines (bands)?
- The bonds that hold molecules together are destroyed in hotter stars.
- The hotter stars have larger molecules.
- The cooler stars have vastly different amount of hydrogen and helium.
- Color depends on what characteristic of light?
- wavelength
- amplitude
- brightness
- mood
- An excited atom decays to its ground state and emits a photon of green light.
If instead the atom decays to some intermediate state, then the light emitted could be which of the following?- violet
- blue
- red
- An excited atom decays to some intermediate state and emits a photon of yellow light.
If instead the atom decays all the way to the ground state, then the light emitted could be which of the following?- blue
- orange
- red
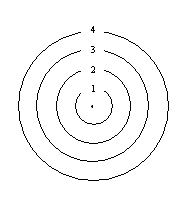
A hypothetical atom has four distinct energy states.
Assuming all transitions are possible, how many spectral lines can this atom produce?- six (4 to 1, 4 to 2, 4 to 3, 3 to 2, 3 to 1, 2 to 1)
- four (4 to 1, 3 to 1, 2 to 1, 1 to nucleus)
- seven (4 to 1, 4 to 2, 4 to 3, 3 to 2, 3 to 1, 2 to 1, 1 to nucleus)